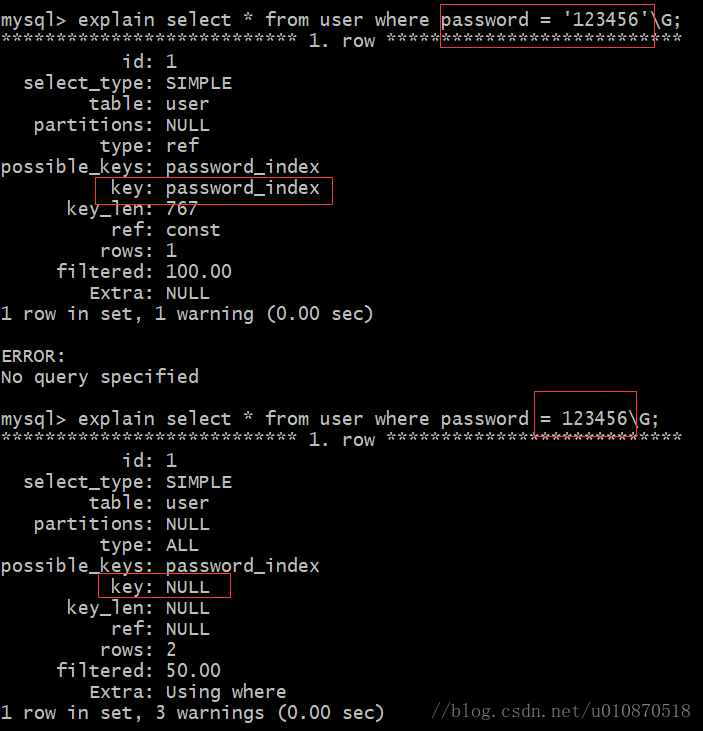
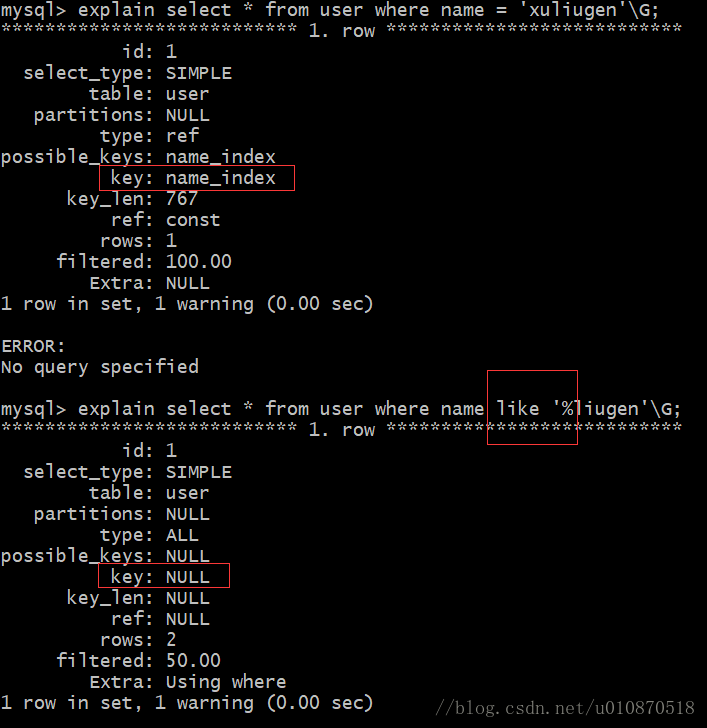
stream
stream分组去重合并
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
输出:[Buss{name='a', count=10, value=0.3}, Buss{name='b', count=33, value=4.0}, Buss{name='c', count=25, value=2.1}]
如何根据两个字段排序,可以再model里面,写一个类似的方法即可,下例,分组的key 就是name+value1
2
3public String groupField() {
return getName()+"-"+getValue();
}
stream分组去重求最大值
List对象筛选学生年龄和性别一样的进行分组,并且挑选出身高最高的学生1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private Long hight;
private int sex;
public Student(String name, int age, long hight, int sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hight = hight;
this.sex = sex;
}
//省去相应get/set方法
//设置年龄和性别的拼接,得出相应分组
public Long getIwantStudent(){
return Long.valueOf(this.sex + this.age);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> allList = new ArrayList<>();
allList.add(new Student("韩梅梅",20,178L,1));
allList.add(new Student("马冬梅",20,168L,1));
allList.add(new Student("李磊",21,179L,2));
allList.add(new Student("小李",21,189L,2));
//以年龄和性别分组,并选取最高身高的学生
Map<Long, Optional<Student>> allMapTask = allList.stream().collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getIwantStudent,
Collectors.maxBy((o1, o2) ->
o1.getHight().compareTo(o2.getHight()))));
//遍历获取对象信息
for (Map.Entry<Long,Optional<Student>> entry: allMapTask.entrySet()) {
Student student = entry.getValue().get();
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}
其中代码可以改写:1
2
3Map<Long, Optional<Student>> allMapTask = allList.stream().collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getIwantStudent,
Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Student::getHight))));
注意:
Collectors.groupingBy方法根据Student对象中方法作为分组条件
Collectors.maxBy方法筛选每个分组中符合条件的数据
stream分组
思考一下Employee对象流,每个对象对应一个名字、城市和销售数量,如下表所示:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8+----------+------------+-----------------+
| Name | City | Number of Sales |
+----------+------------+-----------------+
| Alice | London | 200 |
| Bob | London | 150 |
| Charles | New York | 160 |
| Dorothy | Hong Kong | 190 |
+----------+------------+-----------------+
在Java8中,你可以使用groupingBy收集器,像这样:Map<String, List<Employee>> map = employees.stream().collect(groupingBy(Employee::getCity));
结果如下面的map所示:{New York=[Charles], Hong Kong=[Dorothy], London=[Alice, Bob]}
还可以计算每个城市中雇员的数量,只需传递一个计数收集器给groupingBy收集器。第二个收集器的作用是在流分类的同一个组中对每个元素进行递归操作。Map<String, Long> map = employees.stream().collect(groupingBy(Employee::getCity, counting()));
结果如下面的map所示:{New York=1, Hong Kong=1, London=2}
另一个例子是计算每个城市的平均销售,这可以联合使用averagingInt和groupingBy 收集器:Map<String, Double> map = employees.stream().collect(groupingBy(Employee::getCity, averagingInt(Employee::getNumSales)));
结果如下map所示:{New York=160.0, Hong Kong=190.0, London=175.0}
Java8的foreach()中使用return,不能使用break/continue
使用foreach()处理集合时不能使用break和continue这两个方法,也就是说不能按照普通的for循环遍历集合时那样根据条件来中止遍历,而如果要实现在普通for循环中的效果时,可以使用return来达到,也就是说如果你在一个方法的lambda表达式中使用return时,这个方法是不会返回的,而只是执行下一次遍历。
代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7List<String> list = Arrays.asList("123", "45634", "7892", "abch", "sdfhrthj", "mvkd");
list.stream().forEach(e ->{
if(e.length() >= 5){
return;
}
System.out.println(e);
});
输出:1
2
3
4123
7892
abch
mvkd
return起到的作用和continue是相同的